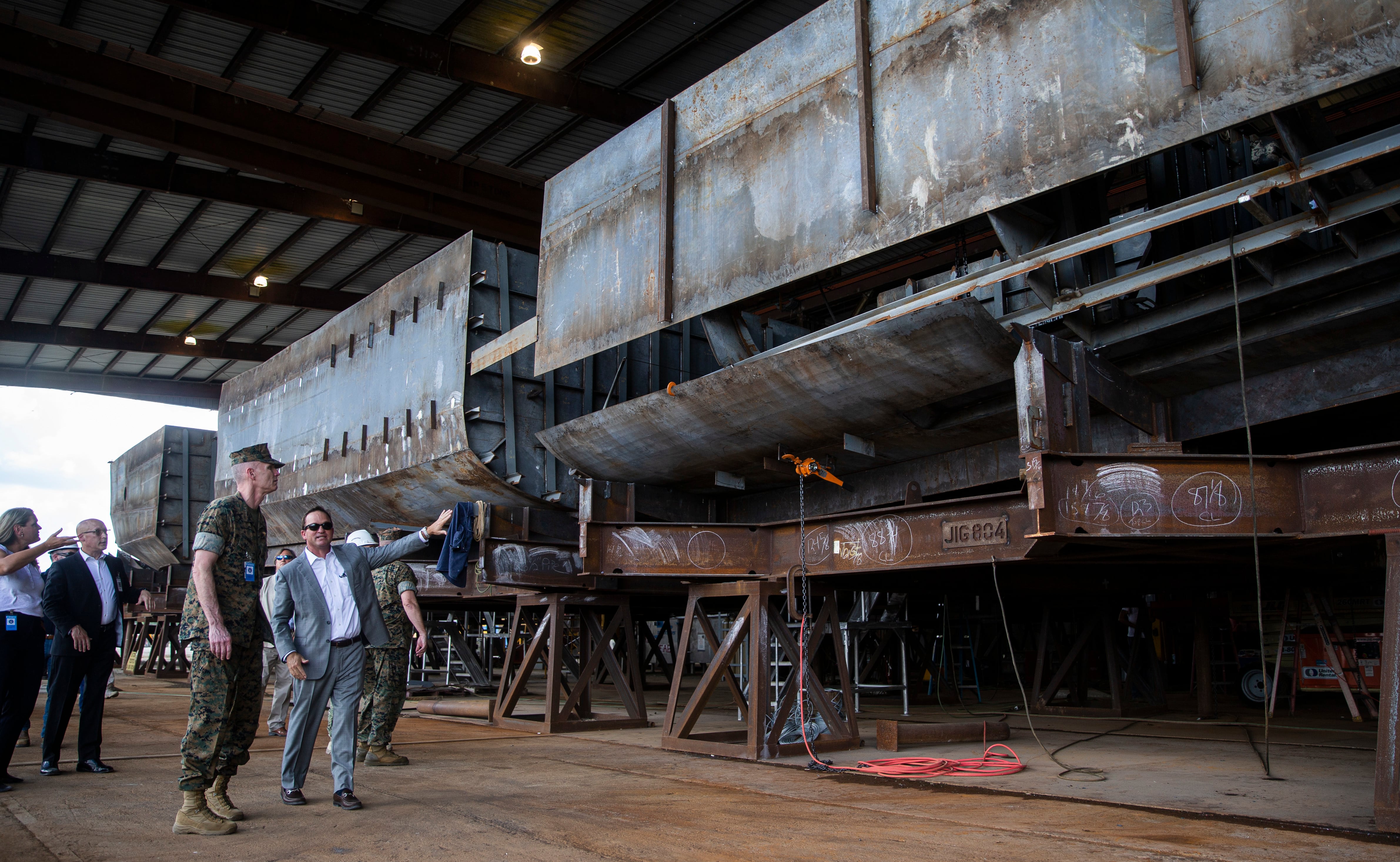
The U.S. Navy has ordered the builder of its Landing Craft Utility 1700 program to stop work and moved to terminate the contract, the shipbuilder Swiftships told Defense News, following years of challenges and disagreements on the program.
The yard has laid off nearly 100 workers related to the LCU program since January and is considering actions to dispute the Navy’s termination of the contract, hoping to get back into a settlement process.
Louisiana-based small business Swiftships won the LCU competition in March 2018, with the Navy awarding a contract for $18 million for the detail design and the construction of the first craft. The yard also received follow-on contracts, one in 2019 worth $26.7 million for the next two craft, and another in 2020 worth $50.1 million for four more.
These craft haul Marines as well as their ground equipment and weapons from amphibious ships to the shore and back again. They are the slower but heavier-lift connectors, compared to the Ship to Shore Connectors that travel at higher speeds but carry less weight.
Swiftships’ contract called for options to build as many as 32 — the total number of craft needed to replace the Navy’s Vietnam-era LCU inventory.
In September 2023, the Navy awarded another LCU contract to Alabama-based Austal USA. The contract called for building three craft for $91.5 million — a significantly higher per-unit cost than Swiftships’ contract — and options for another nine.
According to interviews with and documentation provided by Swiftships, Naval Sea Systems Command on Nov. 9 raised the possibility of terminating the program.
NAVSEA wrote that the shipyard was not making progress on LCU production and offered to reach a settlement that would include Swiftships turning over parts and material delivered by its vendors. On Jan. 24, NAVSEA issued a stop-work order on the program, according to documentation provided by Swiftships, and on Feb. 20 the command formally notified the yard of its decision to terminate the contract.
In its notification to Swiftships, NAVSEA wrote the first three craft were supposed to be delivered by June, September and December 2023, but are still incomplete. NAVSEA declined to comment to Defense News.
Years of challenges
Swiftships’ chief executive, Shehraze Shah, told Defense News there had long been turbulence in the program. Indeed, he said, the Navy and Swiftships had not agreed on a final design two years into the program, and a third-party design agent was brought in to complete the design but continued to make changes. Shah pointed to these issues as reasons the construction could not move forward on time.
Jeff Leleux, the president of the yard, said the Navy and Swiftships took nearly a year to settle a request for equitable adjustment — needed to realign the cost and schedule associated with the contract due to the delays — during which Swiftships and its vendors went months without payment.
After the new timeline was set, said John Messinger, Swiftships’ director of proposals and contracts, the yard realized one of the design changes made by the third-party design agent would require the company to rip out the engine-cooling system and reinstall some piping on the craft, for example.
The executives said they are behind schedule, but contend the Navy has not negotiated with them in good faith amid design and supply chain challenges.
The issue caught the attention of lawmakers far earlier. In September 2022, Republican Reps. Clay Higgins of Louisiana and Neal Dunn of Florida wrote a letter to the secretaries of the Navy and the Department of Homeland Security to discuss their concerns about work being taken from smaller yards and given to Austal USA.
“In addition to delays caused by the COVID-19 pandemic,” the letter read, “SwiftShips notified Congress regarding unnecessary complications with the Navy’s handling of the LCU-1700 contract. These complications include four program manager transitions since the signing of the contract, needless stop work orders, delayed payments to SwiftShips and material vendors, and serious design delays. SwiftShips has continuously struggled with the acquisition of materials due to the Navy ceding its contractual obligation to pay material vendors.”
The letter stated the Navy notified Congress in April 2022 of its intention to award Austal the LCU work without formally re-competing the program, even though Austal at that time had not yet opened its steel ship production line. The Alabama yard had previously only constructed aluminum ships, but began establishing a steel construction line following a $50 million Defense Production Act grant in 2020.
Megan Eckstein is the naval warfare reporter at Defense News. She has covered military news since 2009, with a focus on U.S. Navy and Marine Corps operations, acquisition programs and budgets. She has reported from four geographic fleets and is happiest when she’s filing stories from a ship. Megan is a University of Maryland alumna.