MOSCOW — Russian President Vladimir Putin on Monday marked the fifth anniversary of Russia’s annexation of Crimea from Ukraine by visiting the Black Sea peninsula.
Putin began his trip by attending the launch of new power plants in Crimea, part of Moscow's efforts to upgrade the region's infrastructure.
Ukraine has cut off energy supplies to the peninsula and blocked shipments of Crimea-bound cargo via its territory after Moscow annexed the region in 2014.
"The situation has changed radically," Putin said, adding that the new power facilities will fully cover Crimea's needs.
Russia’s modernization effort has included the construction of a 19-kilometer (11.8-mile) bridge which opened last year across the Kerch Strait that links the Black Sea and the Sea of Azov.
The $3.6-billion project gave Crimea a land link to Russia. Previously, ties between the two depended on a ferry crossing that was often interrupted by gales.
Russia's annexation of Crimea drew U.S. and EU sanctions against Russia. On Monday, NATO and the European Union reaffirmed their strong condemnation of the land grab.
NATO allies said in a statement that “we strongly condemn this act, which we do not and will not recognize.”
They also criticized Russia’s military buildup in Crimea and alleged rights abuses including “arbitrary detentions, arrest, and torture” against members of the Crimean Tartar community.
RELATED

EU foreign policy chief Federica Mogherini said “we stand in full solidarity with Ukraine, supporting its sovereignty and territorial integrity.”
NATO and the EU also called for the release of Ukrainian seamen who were seized by Russia in November's standoff in the Black Sea.
Putin claims that Russia "re-integrated" Crimea after the ouster of Ukraine's former pro-Russian president in 2014 to protect ethnic Russians who made up the majority of Crimea's population from Ukrainian nationalists. The Kremlin was also worried that a new Ukrainian government could annul Russia's lease on its key Black Sea navy base in Crimea and welcome NATO there instead.
Crimea was first seized by Russian forces in the 18th century under Catherine the Great.
The 27,000-square kilometer (10,425-square mile) territory, roughly the size of Massachusetts, became part of Ukraine in 1954 when Soviet leader Nikita Khrushchev transferred jurisdiction from Russia, a move that was a mere formality until the 1991 collapse of the Soviet Union meant that Crimea landed in an independent Ukraine.
The Kremlin has argued that Khrushchev's move violated then-Soviet law, making the transfer illegitimate.
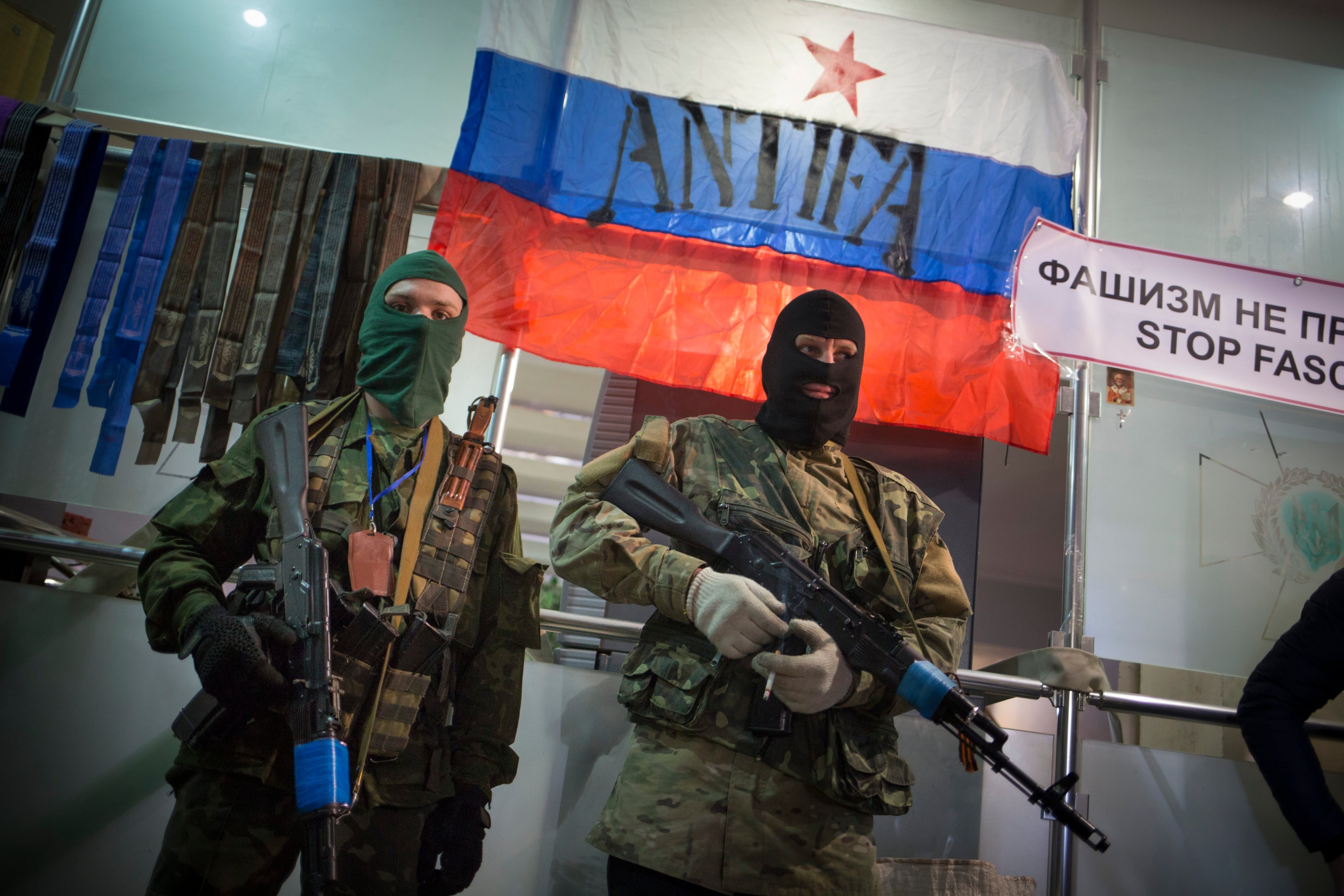

Russian troops swept Crimea just days after the February 2014 ouster of Ukraine’s Russia-friendly president, catching the West by surprise.
The Russian forces blocked Ukrainian soldiers at their garrisons, setting the stage for a hastily-called referendum in Crimea that the West denounced as illegitimate.
Putin said he put Russia's nuclear forces on combat readiness during the 2014 developments in Crimea and warned his Western counterparts that Moscow was ready to defend what it considered its land.
The annexation gave Russia hundreds of miles of coastline along the Black Sea, a near-stranglehold on commerce in the Sea of Azov and access to vast amounts of potential energy riches on the Black Sea shelf.
The U.S. and the EU responded to the annexation of Crimea and Moscow's support for a separatist insurgency in Ukraine's east with waves of sanctions that have limited Russia's access to global financial markets and to energy and defense technologies. The Kremlin fired back by cutting imports of most Western food.
The annexation of Crimea, a lush peninsula which long has been a favorite vacation destination for Russians, helped bolster Putin's popularity at home and strengthened Moscow's positions in the Black Sea. However, public enthusiasm in Russia over the grab has worn off over years amid the country's economic difficulties and a plunge in living standards.
A poll conducted earlier this month by the Public Opinion Foundation, a Moscow-based survey firm, showed that most Russians continue to support the annexation, but also indicated an increasing public awareness of its costs.
The nation-wide survey of 1,500 had 46 percent of respondents saying the seizure of Crimea had a negative impact on the country's international standing, while 26 percent said it had a positive influence and the rest were undecided. It had a margin of error of no more than 3.6 percentage points.
Lorne Cook contributed from Brussels.